Spring Framework基础
Spring简介
Spring 框架的核心特性就是可以用于开发任何Java程序,但是在JEE平台上构建web应用长须是需要扩展的。
Sprint Framework是所有框架的基础,所有的Spring框架均是建立在Spring Framework 的基础上的。
注意打包方式一定要是jar,否则resource下的文件不会被打包到target 下。
<packaging>jar</packaging>
特性
- 非侵入式:对原生技术和领域模型是零污染。
- 控制反转IOC:反转资源获取方向,将自己创建资源、向环境索取资源 → 环境将资源准备好、我们享受资源注入(降低对象与对象的依赖关系)。
- 面向切面AOP:在不修改源代码的基础上,将容器内对象替换成代理类,再完成注入 → 增强代码功能。
- 容器:
SpringIOC是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理组件的生命周期。组件享受到了容器化的管理,替程序员屏蔽了组件创建过程中的大量细节,极大降低了使用门槛。 - 声明式:很多以前需要编写代码才能实现的功能,现在只需要声明需求即可由框架代为实现的。
- 组件化:组件即放在容器当中
bean,并且使用注入完整组件的组装。 - 一站式:在
IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的地方库。而且Spring家族系列已经覆盖了广泛的领域,很多方面的功能性需求可以在Spring Framework的基础上全部使用Spring来实现。
五大功能模块 (仅仅是Spring Framework)
| 功能模块 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| Core Container | 核心容器、在Spring环境下使用任何功能都必须基于IOC容器。 |
| AOP & Aspects | 面向切面编程 |
| Testing | 提供了对Junit 或 TestNG 测试框架的整合 |
| Data Access / Integration | 提供了对数据访问/集成的功能 (SpringJDBC) |
| Spring MVC | 提供了面向Web应用程序的集成功能 |
IOC(非常非常重要!!!)
思想
以前:使用什么资源需要自行创建,创建的细节也需要自己了解。
现在:现在需要使用什么资源,声明一下即可,IOC会自动向声明位置注入资源。(容器推送资源给需要的组件,整合包里面会自动提供资源的创建方式,程序员不用在处理了。)
依赖注入、是IOC的另一种表述方式、是IOC的具体实现,比如setter方式接受容器资源的注入。
IOC在Spring中的实现
- 方式一:
BeanFactory,IOC容器的基本实现,是Spring内部使用的接口。面向Spring本身,不提供给开发人员使用。 - 方式二:
ApplicationContext,BeanFactory的子接口,提供了更多高级的特性。面向Spring的使用者的,几乎所有场合都使用ApplicationContext,而不是底层的BeanFactory。 子类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext使用的是最多的。
ctrl+h可以打开继承了当前类的类的面板
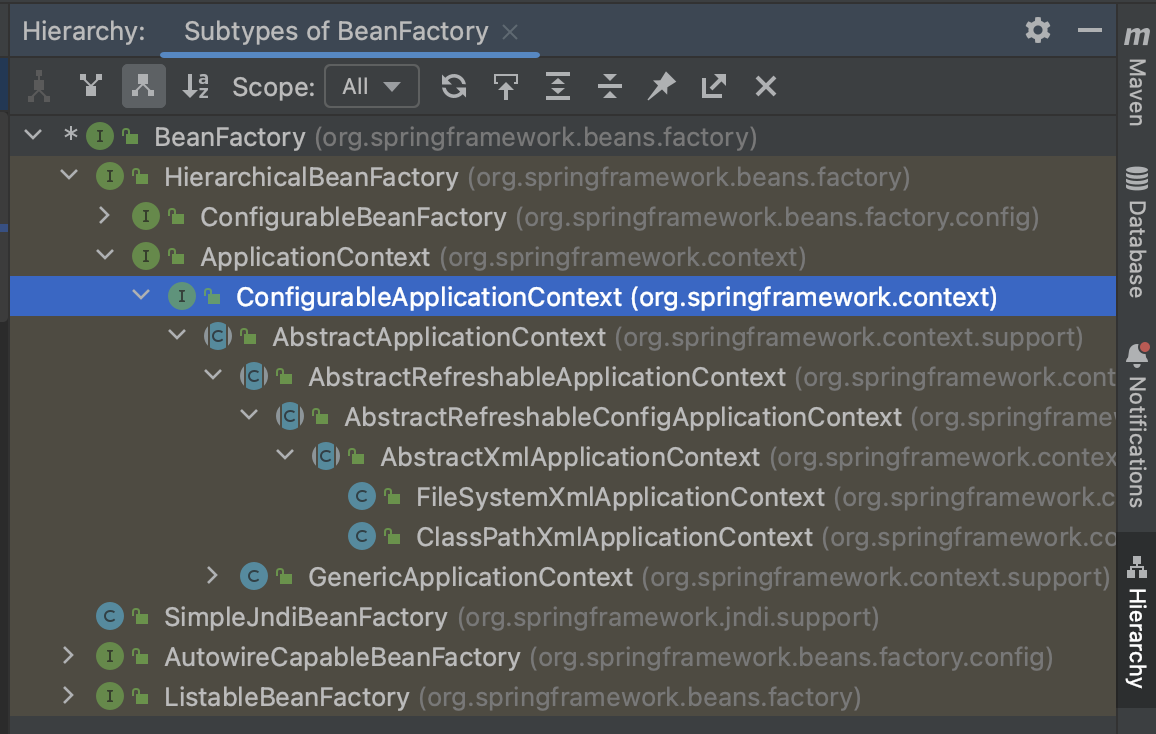
| 类型名 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| FileSystemXmlApplicationContext | 通过读取类路径下的XML配置文件创建IOC容器对象 |
| ClassPathXmlApplicationContext | 通过读取磁盘路径下的XML配置文件创建IOC容器对象 |
| ConfigurableApplicationContext | ApplicationContext的子接口,包含一些扩展方法,让ApplicationContext具有启动、关闭和刷新上下文的能力。 |
| WebApplicationContext | 专门为Web应用准备,基于Web环境创建IOC容器对象,并将对象引入存入ServletContext域中。 |
快速开始
项目依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建spring配置文件
src/main/resources/applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<!--
id : 区分不同的组件, 且IOC容器根据id获取组件
默认单例模式
-->
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
</beans>
测试一下
public class HelloWorldTest {
@Test
public void test(){
// 1. 创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 获取IOC容器中的Bean对象
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld) ioc.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();
}
}
获取Bean的三种方式
- 根据 id获取
- 根据类型获取(这一种使用最多) 当容器当中有多个相同类型的
Bean的时候就GG了。 → 会报NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException错误 id+ 类型的方式(id和类型组合起来唯一就行啦)。
组件实现了接口,同样可以使用接口的类型获得组件,但前提是Bean唯一。
// Student implements Person
// <bean id="student" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student"></bean>
Person person = ioc.getBean(Person.class);
依赖注入
除了这里介绍的以外,依赖注入还有一种**p命名空间**的方式,但注意一般用的不多。
简单数据
setter注入(用的最多)
setter 注入和实体类的 set 方法有关,跟成员变量没有关系。(name属性对应的值就是set方法去掉set并且首字母改为小写的属性。)
<bean id="studentOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<!-- setter 注入 和 set方法有关,跟成员变量没有关系-->
<property name="sname" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
- 构造器注入
<!-- public Student(Integer sid, String sname, Integer age, String gender) -->
<bean id="studentTwo" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg name="sid" value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="sname" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="20"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="gender" value="男"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
根据 <constructor-arg> 标签的顺序来决定调用那个构造参数,name 属性不要省(虽然可以省)
<!-- public Student(Integer sid, String sname, Integer age, String gender) -->
<bean id="studentTwo" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg name="sid" value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="sname" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="20"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="gender" value="男"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
类型数据
-
字面量注入
-
特殊字符,可以使用转义,或
CDATA区。<property name="sname">
<value><![CDATA[ a>b ]]</value>
</property> -
String赋值null
<property name="sname">
<null></null>
</property>
-
-
为类/接口类型的属性复制
-
ref方式:如下:Student类含有一个Course成员,且提供了setter.<bean id="courseOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Course">
<!-- 注入省略 -->
</bean>
<bean id="studentOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<!-- void setCourse(Course course) -->
<property name="course" ref="courseOne"></property>
</bean> -
内部
bean的方式:但是IOC不能获取到内部Bean了。<bean id="studentOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<!-- void setCourse(Course course) -->
<property name="course">
<bean id="courseOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Course">
<property name="cid" value="2222"></property>
<property name="cname" value="远大前程班"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
-
-
数组
-
如果是字面量类型则用
value,如果是类类型则用ref<bean id="studentOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<!-- String[] hobby; -->
<property name="hobby">
<array>
<value>抽烟</value>
<value>喝酒</value>
<value>烫头</value>
<!-- 类类型用 -->
<!-- <ref bean="id"></ref> -->
</array>
</property>
</bean>
-
-
List集合(两种方式)-
方式一
Property标签内部设置,字面量类型用value,类类型用ref<bean id="course" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Course">
<!-- List<Student> students -->
<property name="students">
<list>
<ref bean="studentOne"></ref>
<ref bean="studentTwo"></ref>
<ref bean="studentThree"></ref>
</list>
</property>
</bean> -
方式二 从
List类型的bean注入<bean id="course" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Course">
<!-- List<Student> students -->
<property name="students" ref="studentList"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置一个集合类型的bean -->
<util:list id="studentList" >
<ref bean="studentOne"></ref>
<ref bean="studentTwo"></ref>
</util:list>
-
-
Map集合(两种方式)-
方式一
Property标签内部设置(键是字面量类型则用key属性,类类型则用key-ref)<bean id="teacherOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Teacher"></bean>
<bean id="teacherTwo" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Teacher"></bean>
<bean id="studentOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<!-- Map<String, Teacher> teacherMap; -->
<property name="teacherMap">
<map>
<entry key="teacherOne" value-ref="teacherOne"></entry>
<entry key="teacherTwo" value-ref="teacherTwo"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean> -
方式二 或者从
Map类型的bean注入<util:map id="teacherMap">
<entry key="teacherOne" value-ref="TeacherOne"></entry>
<entry key="teacherTwo" value-ref="teacherTwo"></entry>
</util:map>
<bean id="studentOne" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.Student">
<!-- Map<String, Teacher> teacherMap; -->
<property name="teacherMap" ref="teacherMap"></property>
</bean>
-
Xml Druid数据源
注入依赖
<!-- 数据源依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.31</version>
</dependency>
配置properties
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.23.128:3306/ssm?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=utf-8&autoReconnect=true
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=123456
配置bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- jdbc.properties,引入properties -->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 数据源 : 其实添加的是其一个实现类 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<!-- 数据库信息 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<!-- 连接池设置 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="10"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="16"></property> <!-- 连接池最大活跃连接数 -->
</bean>
</beans>
作用域scope
<bean id="user" class="com.kinda.spring.pojo.User" scope="prototype" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="username" value="kinda"></property>
</bean>
| 取值 | 含义 | 创建对象时机 |
|---|---|---|
| singleton(默认、大部分场景) | 在IOC容器中,这个bean的对象始终为单例 | 容器初始化的时候创建 |
| prototype | 原型模式,获取创建的都是新的对象 | 从容器当中获取的时候创建 |
如果是
WebApplicationContext环境下(Web应用),还有另外两个作用域(但不常用)。
| 取值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| request | 在一个请求范围内有效 |
| prototype | 在一个会话范围内有效 |
bean 的生命周期(重要)

实体类
public class User {
private String username;
public User() {
System.out.println("生命周期1: 反射创建对象默认使用无参构造");
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
System.out.println("生命周期2: 依赖注入");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("生命周期3: 初始化");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("生命周期5: 销毁");
}
}
beans配置项
<bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.User" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<!-- setter 依赖注入 -->
<property name="username" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
测试
@Test
public void test(){
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-lifecycle.xml");
User user = ioc.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
// 容器关闭 -> 出发destroyMethod 方法
ioc.close();
}
前/后置处理器(简单了解)
生命周期调用初始化方法的前后加入额外的处理代码。
容器只能配置一个后置处理器, 针对所有的Bean进行处理。
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之前调用 --> postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之后调用 --> postProcessAfterInitialization");
return bean;
}
}
<bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.User" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<!-- setter 依赖注入 -->
<property name="username" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 后置处理器配置 -->
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.atguigu.spring.processor.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
bean的作用域对生命周期是有影响的。
singleton: 容器创建后立马的执行123, 后续获取直接从4开始,容器关闭调用5。prototype:从容器中获取bean则1, 2, 3, 4 执行,容器关闭不会执行5 , 此作用域对象销毁方法需要用户自己处理。
FactoryBean (重要)
将工厂作为Bean配置到IOC容器当中去,进而可以直接使用IOC容器获得Bean,而不是先获得 Factory.
Bean的创建交给了FactoryBean ,而FactoryBean则交给了IOC创建.
真正交给IOC管理的对象是其从Factory当中返回的bean对象。
好处:Bean的创建很复杂,使用XML完成创建很麻烦
UserFactoryBean的创建
public class UserFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<User> {
@Override
public User getObject() throws Exception {
return new User();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
}
配置文件
<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.factory.UserFactoryBean"></bean>
测试
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-factoryBean.xml");
User user = ioc.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
基于XML的自动装配(重要)
byType
会根据name去匹class
注入类类型(字面量的不行)的时候,XML文件中不在写Property标签和 ref 属性完成注入。
下方演示的将Service使用自动装配的方式注入到 Controller 中
public class UserController {
UserService userService;
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
}
<bean id="controller" class="com.atguigu.spring.controller.UserController" autowire="byType"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.atguigu.spring.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<!-- ... -->
</bean>
上方演示的是byType (用的最多) 方式,其会去容器当中找UserService的实现类,
如果找不到则不装配(即使用默认值);如果找到多个会报 noUniqueBeanDefinitionException。
byName
会根据name去匹配id
byName 基本用不到,我们不用管啦,因为在开发中一个类型的组件只会向容器当中放一次。
当容器当中有多个相同类型能匹配到的时候,可以使用byName进行区分。
基于注解管理Bean
四个注解及其关系
@Component: 将类标识为普通组件@Controller:将类标识为控制层组件@Service:将类标识为业务层组件@Repository: 将类标识为持久层组件
自定义bean的id:@Controller("userController")。
这四个注解功能一摸一样 , 只是给开发人员看(代码可读性),让开发人员区分组件的功能。
四个注解之间的关系 :均由 @Component 扩展出来。
扫描组件
<!-- 组件扫描配置 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring"></context:component-scan>
排除扫描
<!-- 组件扫描配置 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring">
<!--
type: annotation -> 根据注解排除
assignable -> 根据类类型进行排除
如下排除掉控制层的组件
-->
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
包含扫描
默认context:component-scan是use-default-filters="ture" :表示包下的所有的类都需要扫描,需要关掉(false)才能使用包含扫描。
<!-- 组件扫描配置 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring" use-default-filters="false">
<!--
type: annotation -> 根据注解只扫描
assignable -> 根据类类型只扫描
如下只扫描控制层的组件
-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
自动装配注解
Autowire、Qualifier
Autowire默认通过byType的方式,在IOC容器中通过类型匹配某一个bean为属性赋值。
如果有多个类型匹配的bean,此时会自动转换为byName的方式实现自动装配的效果。
如果byType和byName都不行,此时会报错noUniqueBeanDefinitionExceptioin。对应可以通过注解@Qualifier的方式,指定某一个bean的id,将这个bean为属性赋值。
如果IOC容器中没有任何一个类型匹配的bean,此时抛出异常:NoSuchBeanDefinitionException。在@AutoWired注解中有个属性required,默认值为true,要求必须完成自动装配,可以将required设置为false,此时能装配则装配,不能装配则使用默认值。
放置位置
- 放在成员变量上:则Spring会使用暴力反射的方式完成私有属性输入(最常见的用法)
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService service;
}
- 放在
setter方法上:
@Controller
public class UserController {
private UserService service;
@Autowired
public void setService(UserService service) {
this.service = service;
}
}
- 放在有参构造上
代码就不演示了,使用第一种即可啦。
AOP
理念:将非核心逻辑剥离出来以后,封装这些非核心逻辑的类、对象、方法。
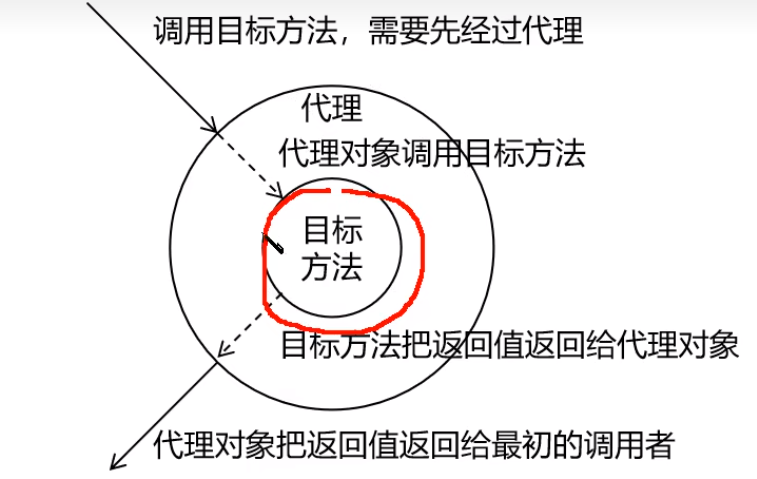
静态代理
代理类需要能够实现所有实体类能够实现的功能,所以代理类和实现类需要继承同一个接口。
CalculatorImpl实现类
package com.kinda.spring.proxy;
public class CalculatorImpl implements Calculator{
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("日志:"+"方法内部");
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("日志:"+"方法内部");
return result;
}
}
Calculator接口
package com.kinda.spring.proxy;
public interface Calculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
}
CalculatorStaticProxy代理类
package com.kinda.spring.proxy;
public class CalculatorStaticProxy implements Calculator{
/**
* 这里的target其实就是目标对象,对应这个静态代理类也就是CalculatorImpl类的实例化对象。
*/
private CalculatorImpl target;
public CalculatorStaticProxy(CalculatorImpl target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("日志:"+"方法外部,开始");
int result = target.add(i, j);
System.out.println("日志:"+"方法外部,结束");
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("日志:"+"方法外部,开始");
int result = target.sub(i, j);
System.out.println("日志:"+"方法外部,结束");
return result;
}
}
测试
package com.kinda.spring;
import com.kinda.spring.proxy.CalculatorImpl;
import com.kinda.spring.proxy.CalculatorStaticProxy;
import org.junit.Test;
public class testProxy {
@Test
public void testProxy(){
CalculatorStaticProxy calculatorStaticProxy = new CalculatorStaticProxy(new CalculatorImpl());
int result = calculatorStaticProxy.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
动态代理
实现方式
JDK如上述代码,要求必须要有接口,最终生成的代理类在com.sun.Proxy包下,名为$Proxy2,其和目标类实现的是相同接口。cglib最终生成的代理类会继承目标类,并且和目标类在相同的包下。
不用自己创建代理类java文件(静态代理),而是使用java提供的API生成任意目标类的代理类。
newProxyInstance函数的参数
ClassLoader loader: 指定加载动态生成的代理类的类加载器Class[] interface: 获取目标对象实现的所有接口的class对象的数组InvocationHandler: 设置代理类中的抽象方法如何重写
// 代理工厂
public class ProxyFactory {
private static class Handler implements InvocationHandler{
private Object target;
public Handler(Object proxyedObject) {
target = proxyedObject;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try{
// todo: 执行前添加代码位置
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
// todo: 执行后添加代码位置
} catch(Exception e) {
// todo: 发生异常的位置
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// todo: finally 位置
}
return result;
}
}
public static Object getProxy(final Object target) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new Handler(target));
}
}
AOP一些概念
AOP本身是一种思想,面向切面编程,是面向对象编程的一种补充和完善,它是以通过预编译的方式和运行期动态代理的方式实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加额外功能的一种技术。
一些术语
- 横切关注点:被代理类抽取的非核心业务代码。
- 通知:每个横切关注点都需要对应一个方法实现, 这样的切面类方法就叫通知方法。
- 切面:封装横切关注点的类,就叫切面或封装通知方法类就叫切面。
- 目标:被代理的目标对象。
- 代理:向目标对象应用通知之后创建的代理对象。( 不需要我们自己创建, 而是 AOP 帮我们创建 )
- 连接点(逻辑概念):横切关注点被抽取的位置。
- 切入点:本质就是个表达式,起到定位链接点的作用,将表达式注解到通知上面,进而作用到表示的连接点上面。
总结 : AOP 重点编写切面类(先抽取代码),通过切点表达式声明的方式再套到目标类上告诉Spring框架我要将我注解到的通知应用到那个类的那个连接点上。
作用
- 简化代码:具有重复性(多个类的相同位置)的非核心业务代码抽取,让目标类当中仅剩下简洁的核心业务代码。
- 代码增强:需要切面类里面功能,直接套上去就增强目标类的代码了。
基于注解实现AOP
在Spring的配置文件中开启aop注解功能<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
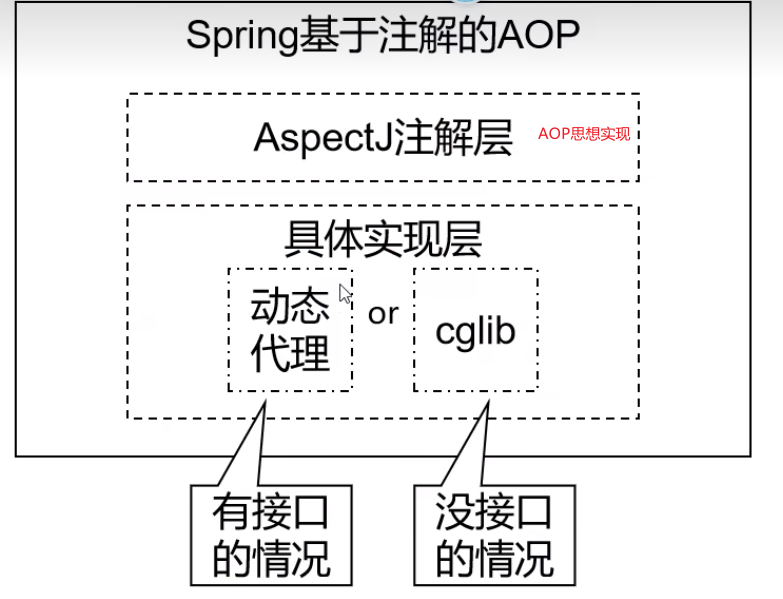
AspectJ:本质上是静态代理, 将代理逻辑“织入”被代理的目标类编译得到的字节码文件,所以最终效果是动态。weaver就是织入器,Spring只是借用了AspectJ中的注解。
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--
AOP 切面类 和 目标类都需要交给 IOC 容器管理
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.aop"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 开启基于注解的AOP功能 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
创建切面类并配置(**)
/**
* 切面类 : 需要注册到IOC容器
*/
@Component
@Aspect // 将组件标识为切面组件
public class LoggerAspect {
// @Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.anno.Calculator.add(int, int))")
// 被增强类的所有的方法
@Before("execution(* com.atguigu.spring.aop.anno.Calculator.*(..))")
public void beforeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("前置方法通知");
}
}
获取连接点的方法信息
@Component
@Aspect // 将组件标识为 切面 组件
public class LoggerAspect {
// 写的太死了
// @Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.anno.Calculator.add(int, int))")
// 被增强类的所有的方法
@Before("execution(* com.atguigu.spring.aop.anno.Calculator.*(..))")
public void beforeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); // 获取方法名称
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); // 获取连接点的参数
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
}
}
切入点表达式的重用
@Component
@Aspect // 将组件标识为 切面 组件
public class LoggerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.spring.aop.anno.Calculator.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void beforeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void afterAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("返回通知");
}
}
返回通知获得返回值
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()", returning = "result")
public void afterAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
System.out.println("返回通知, 且返回值为 : " + result);
}
异常通知获取异常
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowingAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("发生异常" + ex);
}
环绕通知
相当于手动实现动态代理,能代替前面四种通知,且能与前面4种通知共存。一般设置了前面的通知后,就没必要设置环绕通知啦。
/**
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint 可执行的连接点
*/
@Around("pointCut()")
public void aroundAdviceMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知 --> 前置通知");
Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知 --> 返回通知");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕通知 --> 异常通知");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
System.out.println("环绕通知 --> 后置通知");
}
}
各种通知的执行顺序
- Spring 5.3.x 版本以前
前置通知 → 目标操作 → 后置通知 → 返回通知/异常通知
- Spring 5.3.x 版本以后 ( 当前笔记所作的版本 )
前置通知 → 目标操作 → 返回通知 / 异常通知 → 后置通知
切面优先级
只需要使用注解@Order在切面类的注解上即可,数值越小优先级越高。且默认值是INT_MAX。
@Component
@Aspect // 将组件标识为 切面 组件
@Order(1) // 设置切面的优先级
public class LoggerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.spring.aop.anno.Calculator.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void beforeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void afterAdviceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("返回通知");
}
}
基于XML 实现 AOP(了解)
JdbcTemplate
Spring对JDBC进行封装,使用JdbcTemplate方便实现数据库操作.
依赖
<!-- spring 核心: IOC 的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.31</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring jdbc 和 spring-tx 事务 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring 整合Junit 的包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
spring IOC容器配置文件
<!-- jdbc.properties -->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 数据源 : 其实添加的是其一个实现类 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<!-- 数据库信息 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<!-- 连接池设置 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="10"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="16"></property> <!-- 连接池最大活跃连接数 -->
</bean>
<!-- 注册 JDBCTemplate : 第三方Jar包使用不了注解 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
测试 spring-test
spring 和 junit 的整合包,可以让测试环境直接在IOC容器中开始,不用每次测试去创建IOC容器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
// 指定测试环境的核心配置文件
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class jdbctemplateTest {
// 注入 JdbcTemplate
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 查询插入
*/
@Test
public void testInsert(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO t_user VALUES (null, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "root", "123456", 23, "女", "123@qq.com");
}
/**
* 测试查询单个对象
*/
@Test
public void testGetUserById(){
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE id = ?";
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 5);
System.out.println(user);
}
/**
* 测试查询所有
*/
@Test
public void testGetAllUser(){
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_user";
List<User> users = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* 单行单列查询
*/
@Test
public void testGetCount(){
String sql = "SELECT count(*) from t_user";
Integer integer = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
事务(重点)
编程式事务
- 细节没有被屏蔽:所有细节都要程序员自己来实现,比较繁琐。
- 代码复用性不高:没有有效抽取出来,每次实现功能都需要自己编写代码,代码没有得到复用。
try {
// 开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 核心操作
// 提交事务
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 回滚事务
conn.rollback();
} finally {
// 资源回收 或 归还链接到连接池中
conn.close();
}
声明式业务
Spring中实现事务的切面和通知已经写好(事务管理器),我们只需要使用@Transaction来标记需要套的连接点。
IOC配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring"></context:component-scan>
<!-- jdbc.properties -->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 数据源 : 其实添加的是其一个实现类 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<!-- 数据库信息 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<!-- 连接池设置 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="10"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="16"></property> <!-- 连接池最大活跃连接数 -->
</bean>
<!-- 注册 JDBCTemplate : 第三方Jar包使用不了注解 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注册 事务管理器 : 是个切面类 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 注入数据源:链接均从数据源当中获取 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务的注解驱动 : 将环绕通知作用到连接点上,即 @Transactional 标记的类 或 方法使用事务管理 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
测试
场景模拟:买书操作
- 先查询图书价格。 → 2. 更新图书库存。 → 3. 更新用户余额。
其中2,3环节余额不足的时候就会触发事务的回滚。
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 我們不做数据的检验和抛出异常, 借助数据库 unsigned 类型抛出异常
* @param userId
* @param bookId
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
// 查询图书的价格 和 用户余额
Integer bookPrice = bookDao.getPriceById(bookId);
Integer userBalance = userDao.getBalanceById(userId);
// 更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
// 更新用户的余额
userDao.updateBnlance(userId, userBalance - bookPrice);
}
}
事务属性
- 只读
对一个查询操作来说,我们设置成只读(默认false),就能明确告诉数据库这个操作不涉及写操作。这样数据库针对查询操作就能进行优化。
如果事务内部涉及到任何增删改,则会报错:SQLException:Connection is read-only。
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
// 查询图书的价格 和 用户余额
Integer bookPrice = bookDao.getPriceById(bookId);
Integer userBalance = userDao.getBalanceById(userId);
// 更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId); // 有修改操作:报错
// 更新用户的余额
userDao.updateBnlance(userId, userBalance - bookPrice);
}
- 超时
事务当中程序阻塞住了,从而长时间占用数据库资源(大概率是java程序或者MySQL数据库链接等等)。这个时候设置超时,可以在规定时间到达后立马回滚,将资源释放出来,并抛出 TransactionTimedOutException 。
@Override
@Transactional(timeout=3) // 设置超市时间为 3S
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
@Override
@Transactional(timeout = 3)
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 查询图书的价格 和 用户余额
Integer bookPrice = bookDao.getPriceById(bookId);
}
}
- 回滚策略
声明式事务默认只针对运行时异常回滚,编译时异常不会滚。
@Override
@Transactional(
noRollbackFor = {ArithmeticException.class} // 1/0 的运行异常被排除出去,事务依然执行成功
)
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
// 查询图书的价格 和 用户余额
Integer bookPrice = bookDao.getPriceById(bookId);
Integer userBalance = userDao.getBalanceById(userId);
// 更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
// 更新用户的余额
userDao.updateBnlance(userId, userBalance - bookPrice);
System.out.println(1/0); // 抛出 数学运行时异常 会导致事务回滚, 但是事务内的操作应该是执行成功了,因此遇见此异常不回滚
}
- 隔离级别
| 隔离级别 | 中文 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITED | 读未提交 | 有 | 有 | 有 | |
| READ COMMITTED | 读已提交 | 无 | 有 | 有 | |
| PEREATABEL READ | 可重复读 | 无 | 无 | 有 | |
| SERIALIZABLE | 串行化 | 无 | 无 | 无 |
可重复读会读事务内正在读取的数据加锁(行锁),其他事务的更新提交会进入阻塞状态,直到前者事务提交。但是不影响后者对其他行修改或添加数据。但是MySQL的REPEATABLE_READ解决了幻读的问题。
这一环节有大量较难的数据库相关知识,有待补充。
@Override
@Transactional(
isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ // 修改为可重复读(其实就是MySQL的默认的隔离级别)
)
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
// 查询图书的价格 和 用户余额
Integer bookPrice = bookDao.getPriceById(bookId);
Integer userBalance = userDao.getBalanceById(userId);
// 更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
// 更新用户的余额
userDao.updateBnlance(userId, userBalance - bookPrice);
}
- 传播行为(重要)
A方法调用B方法,且两者都声明了事务,我们从B的角度来思考:
- B使用自己的事务:如果B回滚了,不会导致或者说是影响A的回滚。
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW - B使用A的事务:如果B发生回滚了,则A也发生回滚。
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED
/**
* 我們不做数据的检验和抛出异常, 借助数据库 unsigned 类型抛出异常
* @param userId
* @param bookId
*/
@Override
@Transactional(
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED
)
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
// 查询图书的价格 和 用户余额
Integer bookPrice = bookDao.getPriceById(bookId);
Integer userBalance = userDao.getBalanceById(userId);
// 更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
// 更新用户的余额
userDao.updateBnlance(userId, userBalance - bookPrice);
}
/**
* 买多本书
* @param userId
* @param bookIds
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public void checkout(Integer userId, Integer[] bookIds) {
for(Integer bookId : bookIds) {
buyBook(userId, bookId);
}
}
基于XML的事务
用的很少,用到的时候来看下就好了。
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务的切面 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 考虑到后面整合 SpringSecurity, 避免把 UserDetialsService 扫描到事务控制,因此让切入点表达式定位到 impl -->
<aop:pointcut id="txPointcut" expression="execution(* *..*ServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 将切入点表达式 和 事务的通知关联起来 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut" />
</aop:config>
<!-- 配置事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<!-- 配置事务的属性 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 查询方法:配置只读属性,让数据库知道这是一个查询操作 -->
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="query*" read-only="true"/>
<!-- 增删改查方法:配置下事务的传播行为、回滚异常
rollbackfor:
默认:运行时异常
建议:编译时异常和运行时异常都回滚.
-->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="Exception"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="Exception"/>
<tx:method name="remove*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="Exception"/>
<tx:method name="batch*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="Exception"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>